best test for ovarian torsion|ovarian torsion vs ectopic pregnancy : tv shopping Ovarian torsion is a surgical emergency. Rapid diagnosis and intervention are necessary to preserve ovarian function where this is clinically appropriate and it is important to . WEB7 de ago. de 2021 · Description: In this short F-series game you'll see Nami. She'll undress and play a little bit with herself using big dildo. Click on the icon at the top left side. Then use blue arrow buttons on the sides to progress the scene. Version: Updated: 2021-08-07, Posted: 2016-05-26. Request for an Update!
{plog:ftitle_list}
Sobre o GNDI O Grupo O Grupo Em destaque. . Resultado de Exame Resultados Resultados Rede de Atendimento . Rede de Atendimento Rede Assistencial .
Ovarian torsion is a surgical emergency. Rapid diagnosis and intervention are necessary to preserve ovarian function where this is clinically appropriate and it is important to . Ovarian torsion (or adnexal torsion) is a twisting of the ovary (and/or fallopian tube) on its vascular and ligamentous supports, blocking adequate blood flow to the ovary. . Accuracy of the preoperative diagnosis in 100 emergency laparoscopies performed due to acute abdomen in nonpregnant women. The accuracy of serum interleukin-6 and .
ミッシェル 水分 計
Ovarian torsion occurs when an ovary becomes twisted around its supporting tissues. Find out why this happens, how to recognize the symptoms, and more. CT and MRI are not generally used to diagnose ovarian torsion but are commonly done to rule out other abdominal pathology such as acute appendicitis. The definitive . While age plays a role, ovarian torsion can occur unexpectedly and may require an emergency visit to your doctor. Here's what you need to know about this condition, . Ovarian torsion is a gynaecological emergency: a delay in diagnosis and referral can lead to a reduction in fertility. Ovarian masses are the most common cause of ovarian torsion, but torsion can occur in their .
Ovarian torsion - Knowledge @ AMBOSS provides information on the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of ovarian torsion.
If you have risk factors for ovarian torsion or your OB-GYN suspects it, they will likely perform medical tests. These may include: Blood tests: The OB-GYN may use this approach to check for an infection or signs of a hemorrhage. Pregnancy test: Pregnancy is an ovarian torsion risk factor, so it is useful to confirm it or rule it out. Doppler ultrasound: This .Aim: The aim of this study is to evaluate the diagnostic value of serum oxidative stress marker levels (ischemia-modified albumin, IMA; malondialdehyde, MDA) and total oxidant status (TOS), total antioxidant status (TAS) and oxidative stress index (OSI) levels that occur in ovarian torsion and to determine the threshold value of these markers in the diagnosis of ovarian torsion. Ovarian Torsion is a true gynaecological emergency that requires urgent surgical intervention to prevent ovarian necrosis. . Blood tests: 1. FBE: . The next best option – in particular for children – is a transabdominal ultrasound, preferably with a full bladder, (however there should not be excessive delays in attempting to achieve a .
Ovarian torsion is the rotation of the ovary and portion of the fallopian tube on the supplying vascular pedicle; Referred to as adnexal torsion and tubo-ovarian torsion; Occurs in females of all ages Most common in reproductive age adults; In children, it is most common in 9-14 years of age; Risk factors: Ovarian mass; Fertility treatments OBJECTIVE. The CT and MRI features of ovarian torsion are illustrated with gross pathologic correlation. Ovarian enlargement with or without an underlying mass is the finding most frequently associated with torsion, but it is nonspecific. A twisted pedicle, although not often detected on imaging, is pathognomonic when seen. Subacute ovarian hemorrhage .Article 1: Ovarian Torsion: A Fifteen-Year Review, Ann Emerg Med 2001; 38: 156-159 ANSWER KEY. Article 2: Ovarian torsion: 10-year perspective, Emergency Medicine Australasia 2005; 17: 231–237 ANSWER KEY. Article 3: Emergency laparoscopy for suspected ovarian torsion: are we too hasty to operate? Fertility and Sterility 2010; 93: 2012-2015 OBJECTIVE. The CT and MRI features of ovarian torsion are illustrated with gross pathologic correlation. Ovarian enlargement with or without an underlying mass is the finding most frequently associated with torsion, but it is nonspecific. A twisted pedicle, although not often detected on imaging, is pathognomonic when seen. Subacute ovarian hemorrhage .
Ovarian torsion. Cysts can grow so big that they distort the shape of your ovary, increasing the likelihood that it’ll twist. The twisting can prevent blood flow to your ovary, causing it to die. Extreme pain, nausea and vomiting are all signs of ovarian torsion.
Ovarian torsion rarely presents with classic symptoms. Always consider torsion when evaluating a female patient with abdominal pain, back pain, or flank pain. While US is a great first initial test for the evaluation of both ovarian torsion, do not be reassured by normal dopplers. The most common finding is an ovary > 4cm. CT may as sensitive . Ovarian torsion is when an ovary twists around its own ligaments. People should seek urgent medical care for ovarian torsion. . To diagnose ovarian torsion, a doctor may use the following tests . ### What you need to know A 35 year old woman presents to her local emergency department with intermittent episodes of severe left iliac fossa pain over a few weeks. The pain is increasing in intensity and associated with vomiting and fainting or dizziness. She is also 10 weeks pregnant. Ovarian torsion is a gynaecological emergency characterised by the ovary .
Ovarian torsion refers to complete or partial rotation of the adnexal supporting organ with ischemia. It can affect females of all ages. Ovarian torsion occurs in around 2%–15% of patients who have surgical treatment of adnexal masses. The main risk in .
Ovarian torsion is defined as partial or complete rotation of the ovarian vascular pedicle and causes obstruction to venous outflow and arterial inflow. Ovarian torsion is usually associated with a cyst or tumor, which is typically benign; the most common is mature cystic teratoma. Ultrasonography (US) is the primary imaging modality for evaluation of ovarian .Ovarian torsion (OT) or adnexal torsion is an abnormal condition where an ovary twists on its attachment to other structures, such that blood flow is decreased. [3] [4] Symptoms typically include pelvic pain on one side.[2] [5] While classically the pain is sudden in onset, this is not always the case. [2]Other symptoms may include nausea. [2] Complications may include .
An update on the diagnosis and management of ovarian torsion. Georgios Christopoulos MRCOG, Georgios Christopoulos MRCOG. Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK. Search for more papers by this author. Tony Kelly MRCOG, Tony Kelly MRCOG. Royal Sussex County Hospital, Brighton, UK. Ovarian torsion (adnexal torsion) is an infrequent but significant cause of acute lower abdominal pain in women. . 'Watchful Waiting' Best Approach for Benign Ovarian Cysts; . Test Your Knowledge of Predictive Biomarkers for Ovarian Cancer 0.25 LOC / CME Credits education. You are being redirected to Medscape Education Yes, take me there. 0 . Adnexal torsion is the twisting of the ovary, and often of the fallopian tube, on its ligamental supports, resulting in vascular compromise and ovarian infarction. The definitive management is surgical detorsion, and prompt diagnosis facilitates preservation of the ovary, which is particularly important because this condition predominantly affects premenopausal . Ovarian torsion is an acute condition that can be a true gynecologic emergency. It occurs when an ovary twists on the adjacent infundibulopelvic ligament, causing disruption of blood supply to the ovary and in effect creating a tourniquet. . Best Tests Copy. Subscription Required. Management Pearls Copy. Subscription Required. Therapy Copy .
The overall recurrence rate of ovarian torsion is low, ranging from 2% to 12%; although, reportedly, the rate is higher in spontaneously torsed normal adnexa 48 8. Oophoropexy is controversial and current data are insufficient to support performing an oophoropexy to decrease the risk of recurrent ovarian torsion 47 13 44. Ovarian torsion (adnexal torsion) is an infrequent but significant cause of acute lower abdominal pain in women. . 'Watchful Waiting' Best Approach for Benign Ovarian Cysts; . Test Your Knowledge of Predictive Biomarkers for Ovarian Cancer 0.25 LOC / CME Credits education. You are being redirected to Medscape Education Yes, take me there. 0 . Ovarian torsion is a clinical diagnosis, yet there is a wide variety of presentations and no specific pathognomonic symptom constellation. Most of its clinical signs lack sensitivity and specificity. We miss a lot; Most of the tests we have for torsion aren’t sensitive enough. Even ultrasound, our best option, has around a 27.9% false .A positive pregnancy test does not eliminate the diagnosis of ovarian torsion, especially early in pregnancy, as a corpus luteum cyst may be the source of torsion. . The best initial imaging for ovarian torsion is a transvaginal ultrasound with Doppler. Consult gynecology early if you have a high suspicion for torsion. Differential Diagnosis .
メタノール水分計 dkk
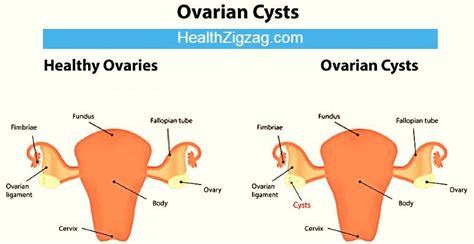
Pelvic adnexal torsion is a collective term referring to twisting of an ovary, fallopian tube, or paraovarian cyst on its axis with varying degrees of vascular compromise. Although it is the fifth most common gynecologic emergency, the diagnosis is challenging and often missed due to symptoms, physical examination findings, and imaging features that are nonspecific. Delay . The adnexa is a set of structures adjacent to the uterus, consisting of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Even though the fallopian tubes are one of the major adnexal structures, this article will focus on the ovaries and the different types of cysts that can form within the ovary. The ovaries are suspended laterally to the uterus via the utero-ovarian ligament, covered by the . Ovarian torsion happens when your ovaries — and sometimes the fallopian tube — twist around the tissue they’re connected to. This cuts off the blood supply to your ovaries, which can cause .The primary risk factor for ovarian torsion is an ovarian mass, particularly a mass that is 5 cm in diameter or larger. Many of the risk factors for ovarian torsion, therefore, are related to the likelihood of developing an ovarian cyst or neoplasm.
twisted or ruptured ovarian cyst
メトラートレド 水分計 点検
risk factors for ovarian torsion
ovarian torsion vs ectopic pregnancy
WEBELISA SANCHEZ BEIJOU,PARTE QUATRO 7 newclipsmarombaELISA SANCHEZ BEIJOU UM FA.
best test for ovarian torsion|ovarian torsion vs ectopic pregnancy